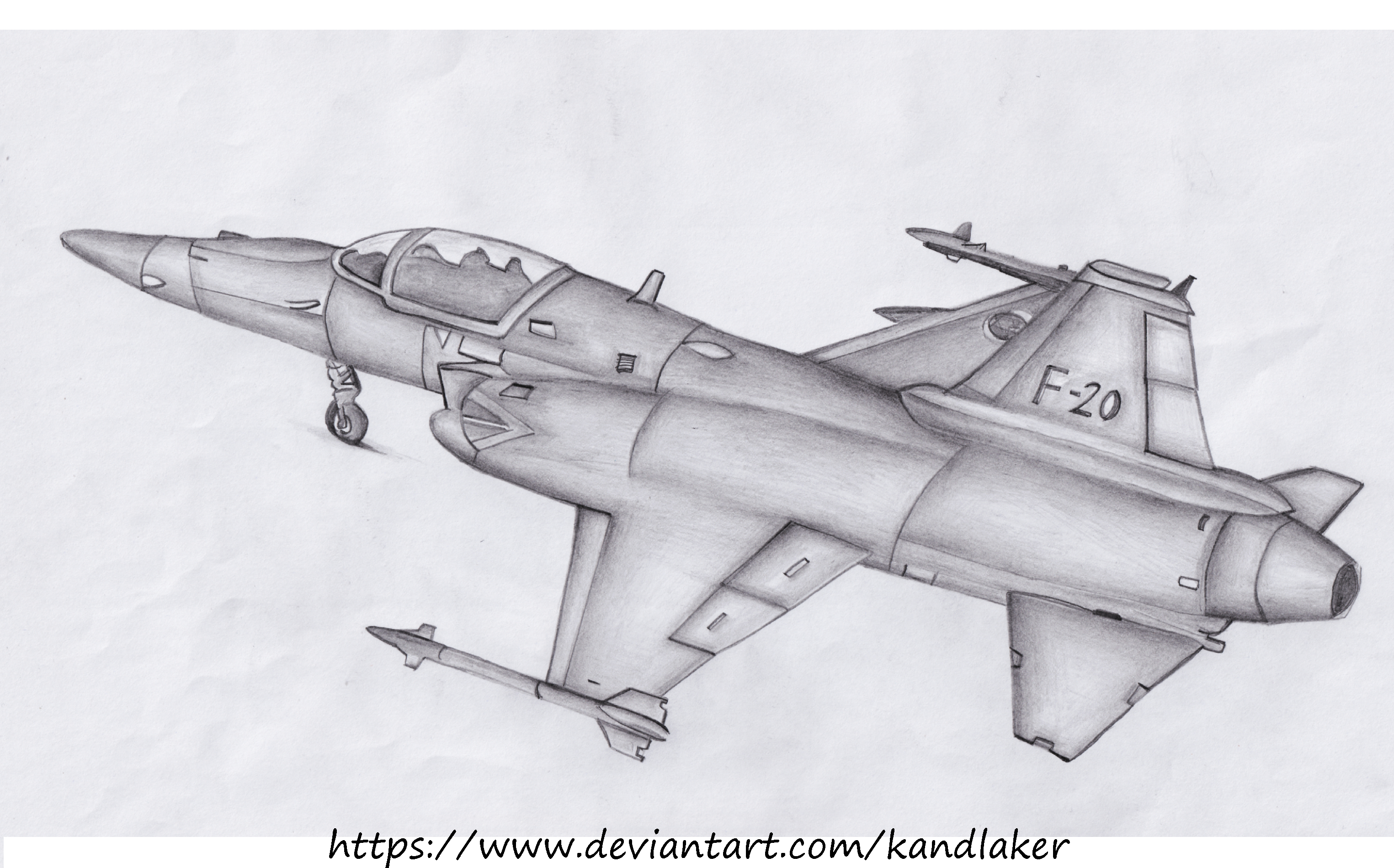
F-20 Fighter Jet - The F-20 Tigershark is a low-cost fighter designed by Northrop but never marketed or mass-produced. The science center's F-20 is the last surviving prototype.
In 1975, Northrop began development of the F-20 Tigershark, a reliable, easy-to-fly and cost-effective fighter jet. Northrop did not receive government funding to develop the aircraft, so the company did not have to look to the Air Force or any other government agency for project decisions. As a result, the development process was very fast. Northrop built three planes to fly around the world for demonstrations for potential customers.
F-20 Fighter Jet

According to many pilots, the Tigershark was an excellent aircraft. It can be ready for combat one minute after takeoff and can climb 53,800 feet per minute. Northrop planned to sell the aircraft to foreign countries for their own military forces. However, due to many political differences and competition from other aircraft such as the F-16, the market for the aircraft never developed.
The F 20 Tigershark And Its Ancestors
The newest version is the F-20 Tigershark prototype on display at the science center. Two other F-20 prototypes have crashed during global sales, but the cause of the crash has not been determined due to aircraft malfunction. The science center's tigershark was donated to the science center by Northrop Corporation. The Northrop F-20 Tigershark (originally F-5G) is a light fighter designed and built by Northrop. Development began in 1975 as a further evolution of Northrop's F-5E Tiger II, with a modern avionics suite that included a new engine that greatly improved overall performance and a powerful and flexible radar. Compared to the F-5E, the F-20 was faster, had higher air-to-air capability, and was equipped with a full suite of air-to-ground systems that could use most of the United States' weapons. With these improved capabilities, the F-20 General Dynamics competed with modern fighter designs such as the F-16 Fighting Falcon, but cost less to purchase and operate.
Most of the F-20 was designated "FX" by the US Department of Defense (DoD). FX attempted to develop fighters that could carry the latest Soviet aircraft, but without considering the advanced technology used by the US Air Force's own aircraft. The FX was a product of the Carter administration's military export policy, which aimed to provide high-quality equipment to foreign countries without the risk of advanced US technology falling into the hands of the Soviets. Northrop had hoped for the F-20 in the international market, but policy changes after the election of Ronald Reagan forced the F-20 to compete for sales against the USAF's newest fighter design, the F-16. . The development program was abandoned in 1986 after three prototypes were built and the fourth partially completed.
John F. Kennedy took office in 1961 and the US Department of Defense was tasked with finding a fighter jet that the US could offer to its allies through the Mutual Defense Assistance Act. Several designs were studied, including older versions of the Lockheed F-104 Starfighter and Vought F-8 Crusader, as well as the newly developed Northrop N-156F. On April 23, 1962, the United States Air Force (USAF)
As the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 became more common, the US Air Force launched the International Fighter Aircraft (IFA) program to give allies equal rights. In the MiG, the USAF wanted a light fighter with competitive capability, mass procurement, and cost-effectiveness for potential customer nations. Although many companies have developed plans, Northrop's current F-5 puts them at the forefront. An upgrade was introduced to the F-5E Tiger II to allow the AN/APQ-153 radar and the AIM-9 Sidewinder missile to be fired from the wing rails. On November 20, 1970, Northrop's test was announced as the IFA winner.
Putin Inspects New Russian Fighter Jet Unveiled At Air Show
In the late 1970s, the Taiwan Air Force of the Republic of China began searching for fighter aircraft to match the upgrades of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Air Force. In particular, they wanted the AIM-7 Hornet, a platform capable of launching long-range missiles. At the time, the United States was about to establish relations with the People's Republic of China after President Nixon's famous visit in 1972. The US viewed China as supporting Taiwan against their interests, and the US State Department wanted to tread carefully. They blocked the export of all AIM-7 capable aircraft except older models of the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II. The State Department offered the Israeli IAI Kaffir instead; But it was rejected.
Taiwan was already producing the F-5E under license, so the Department of Defense asked Northrop to explore adding an AIM-7 capable radar to the Tiger II as an alternative. The effort was the first of several F-5G tests.
In the spring of 1977, the Jimmy Carter administration announced a new military export policy that restricted the sale of these designs to NATO, Australia, and Japan.
Carter said at the time that the United States could not be "the world's champion of peace and the world's leading supplier of weapons of war."
Northrop F 20 Tigershark Aircraft 1 By Bagera3005 On Deviantart
Previously, the United States had no export policy and was concerned that advanced technology might fall into the hands of the Soviets.
Many exceptions were made; Israel and Egypt could buy advanced designs as part of the Base David Accord, and Israel was allowed to buy McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagles, a key piece of US air defense technology. Iran was already acquiring the Grumman F-14 Tomcat, and February 1979 indicated a growing export problem when it was reported that Iran had sold the AIM-54 Phoix missile to the Soviets.
South Korea's F-16 order was initially blocked under this policy, but later allowed in the context of the relationship.
Despite the exceptions, the export policy was implemented and covered a large number of customers. Since the F-5G was slightly inferior to the F-5E, the F-5G appeared to be in a strong position to exceed the limitations imposed on competing designs. However, President Carter personally blocked the sale of the F-5G to Taiwan.
File:f 20 Agressor.jpg
In 1979, export policy problems began to emerge. The Soviets continued to market new aircraft designs to the detriment of their US allies. Countries killed by the US have turned to other equipment for modern fighters, notably France's Dassault Mirage 2000.
Barry N., Assistant Director of the US Office of Arms Control and Disarmament. Blechman said US foreign arms reductions have pleased other countries and increased the global arms trade.
The State Department argued that the US needed a modern counterpart to the role played by the F-5E in the 1960s and 1970s. In response to Carter's questions, they proposed creating a new aircraft based on technology that would not pose a threat to the United States.In January 1980, President Carter authorized the development of a new export fighter: the FX.

The FX should be superior to the F-5E; However, it could not use the advanced air systems used by US aircraft. Unlike the Mutual Defense Assistance Act programs directed at the F-5E, FX will be tirelessly funded. Additionally, companies could not sell aircraft directly; All sales are made by the Department of Defense.
China's J 20 'racing Ahead' Of F 22, F 35 Fighters To Have A Twin Seat Variant To Control Loyal Wingmen Drones
Both Northrop and General Dynamics (GD) have responded to the FX request. GD's F-16/79 was a variant of the F-16A, with the Pratt & Whitney F100 turbofan engine replaced with a J79 turbojet and a reduced airframe;
In 1981, Ronald Reagan's administration gradually eased export restrictions imposed by the Carter administration.
Initially, the FX program continued as usual, but many programs eroded the value of the program and limited sales of the F-5G. The signing of the 1982 US-HHR Joint Memorandum was an important arms trade agreement that prevented the sale of the F-5G to Taiwan. So far, the Taiwanese have launched the AIDC F-CK-1 Ching-kuo light fighter project. When the memorandum was signed, the United States indicated that it would not receive Taiwan's modern aircraft; Accordingly, Ching-kuo received major attention in Taiwan. As a result, sales of the F-5G are still undecided.
In the summer of 1982, Deputy Secretary of Defense Frank Carlucci wrote a memo to the Air Force recommending that foreign customers be solicited to purchase FX aircraft.
Northrop F 20 Tigershark ' Poster By Eng Hadoool
However, four months later, Carlucci issued a secret memo to the same services to eliminate FX and ease the export of front-line fighters overseas.
In December, Carlucci, at the request of the White House, again reversed his position and directed the Air Force to fund a small amount of the F-20 in the fiscal year 1984 budget.
Northrop felt that the F-5G should match the performance of the F-16. This will require not only better performance, but also a new and comparable set of aircraft. Looked at the Northrop F-5G

F 16 fighter jet rides, f 16 jet fighter, toy f 16 fighter jet, f 38 fighter jet, f 86 fighter jet, f 35 jet fighter, us f 35 fighter jet, f 15 fighter jet, j 20 fighter jet, f 36 fighter jet, f 32 fighter jet, f 18 fighter jet
0 Comments